| Principality of Monaco Principatu de Múnegu (Monégasque) Principauté de Monaco (French) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||
| Motto: "Deo Juvante" (Latin) "With God's Help" | ||||||
| Anthem: Hymne Monégasque | ||||||
| on the European continent | ||||||
| Capital | Monaco1[1] 43°43′N 7°25′E / 43.717°N 7.417°E | |||||
| Largest Most populated quartier | Monte Carlo | |||||
| Official language(s) | French[2] is the only official language. Monégasque, Italian and English are also widely spoken and understood. (See Languages of Monaco) | |||||
| Demonym | Monégasque or Monegasque | |||||
| Government | Constitutional monarchy Principality | |||||
| - | Prince | Albert II | ||||
| - | Minister of State | Michel Roger | ||||
| - | President of the National Council | Stéphane Valeri | ||||
| Independence | ||||||
| - | House of Grimaldi | 1297 | ||||
| - | Constitution | 1911 | ||||
| Area | ||||||
| - | Total | 1.98 km2 (232nd) 0.78 sq mi | ||||
| - | Water (%) | 0.0[3] | ||||
| Population | ||||||
| - | 2010 estimate | 30,586[4] (211th) | ||||
| - | 2008 census | 35,352[3] | ||||
| - | Density | 15,142/km2 (1st) 39,217/sq mi | ||||
| GDP (PPP) | 2010 estimate | |||||
| - | Total | $5.888 billion[5][6] (n/a) | ||||
| - | Per capita | $123,811[5][6] (n/a) | ||||
| GDP (nominal) | 2010 estimate | |||||
| - | Total | US$6.972 billion[5][6] (n/a) | ||||
| - | Per capita | US$215,163[5][6] (n/a) | ||||
| HDI (2010) | ||||||
| Currency | Euro (EUR) | |||||
| Time zone | CET (UTC+1) | |||||
| - | Summer (DST) | CEST (UTC+2) | ||||
| Drives on the | right | |||||
| ISO 3166 code | MC | |||||
| Internet TLD | .mc | |||||
| Calling code | +377 | |||||
| 1 | Monaco is a city-state. | |||||
| 2 | GDP per capita calculations include non-resident workers from France and Italy. | |||||
Monaco (![]() i /ˈmɒnəkoʊ/), officially the Principality of Monaco (French: Principauté de Monaco; Monégasque: Principatu de Múnegu; Italian: Principato di Monaco; Occitan: Principat de Mónegue), is a country (and a microstate) located in south western Europe, on the northern central coast of the Mediterranean Sea. It is surrounded on three sides by its neighbour, France, and its centre is about 16 km (9.9 mi) from Italy. Its area is 1.98 km2 (0.76 sq mi) with an estimated population of almost 35,000.
i /ˈmɒnəkoʊ/), officially the Principality of Monaco (French: Principauté de Monaco; Monégasque: Principatu de Múnegu; Italian: Principato di Monaco; Occitan: Principat de Mónegue), is a country (and a microstate) located in south western Europe, on the northern central coast of the Mediterranean Sea. It is surrounded on three sides by its neighbour, France, and its centre is about 16 km (9.9 mi) from Italy. Its area is 1.98 km2 (0.76 sq mi) with an estimated population of almost 35,000.
Monaco is a principality governed under a form of constitutional monarchy, with Prince Albert II as head of state. The House of Grimaldi has ruled Monaco since 1297, and the state's sovereignty was officially recognized by the Franco-Monegasque Treaty of 1861. Despite Monaco being independent, its national defence is the responsibility of France.
Contents[hide] |
[edit] Administrative divisions
[edit] Overview
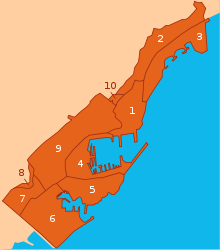
Monaco is the second smallest country (by size) in the world; only the Vatican City is smaller. Monaco is also the world's second smallest monarchy, and one of the most densely populated countries in the world. The state consists of only one municipality (commune). There is no geographical distinction between the State and City of Monaco, although responsibilities of the government (state-level) and of the municipality (city-level) are different. According to the constitution of 1911, the principality was subdivided into three municipalities:
- Monaco (Monaco-Ville), the old city on a rocky promontory extending into the Mediterranean, known as the Rock of Monaco, or simply Le Rocher (the Rock), where the palace is located
- Monte Carlo, the principal residential and resort area with the Monte Carlo Casino in the east and northeast
- La Condamine, the northwest section including the port area, Port Hercule
The municipalities were merged into one in 1917, after accusations that the government was acting according to the motto "divide and conquer" and they were accorded the status of wards (quartiers) thereafter.
- Fontvieille was added as fourth ward, a newly constructed area reclaimed from the sea (in the 1970s)
- Moneghetti became the fifth ward, created from a part of La Condamine
- Larvotto became the sixth ward, created from a part of Monte Carlo
- La Rousse/Saint Roman (including Le Ténao) became the seventh ward, also created from a part of Monte Carlo

Subsequently, three additional wards were created:
- Saint Michel, from a part of Monte Carlo
- La Colle, from a part of La Condamine
- Les Révoires, from a part of La Condamine
An additional ward was planned by new land reclamation, to be settled beginning in 2014; however, Prince Albert II announced in his 2009 New Year Speech that the plans had been put on hold due to the current economic climate.[citation needed]
[edit] Traditional quarters and modern geographic areas
The traditional four quarters of Monaco are: Monaco-Ville, La Condamine, Monte Carlo and Fontvieille. These quarters and Moneghetti are the five "modern geographic areas", defined by the Monaco Department of Tourism which is situated in Monaco-Ville.[7]
[edit] Wards
Currently the principality is subdivided into ten wards (with their official numbers; Le Portier, the proposed ward, was anticipated as number 11):
| No. | Ward | Area (m²) | Population (Census of 2000) | Density km2 | City Blocks (îlots) | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Former municipality of Monaco | ||||||
| 05 | Monaco-Ville | 184,750 | 1,034 | 5597 | 19 | Old City with palace |
| Former municipality of Monte Carlo | ||||||
| 01 | Monte Carlo/Spélugues (Bd. Des Moulins-Av. de la Madone) | 281,461 | 3,034 | 10779 | 20 | the casino and resort area |
| 02 | La Rousse/Saint Roman (Annonciade-Château Périgord) | 105,215 | 3,223 | 30633 | 15 | in the northeast, incl. Le Ténao |
| 03 | Larvotto/Bas Moulins (Larvotto-Bd Psse Grace) | 328,479 | 5,443 | 16570 | 15 | eastern beach area |
| 10 | Saint Michel (Psse Charlotte-Park Palace) | 142,223 | 3,807 | 26768 | 24 | central residential area |
| Former municipality of La Condamine | ||||||
| 04 | La Condamine | 237,283 | 3,847 | 16213 | 27 | port area in the northwest |
| 07 | La Colle (Plati-Pasteur-Bd Charles III) | 188,073 | 2,822 | 15005 | 15 | on the western border with Cap d'Ail |
| 08 | Les Révoires (Hector Otto-Honoré Labande) | 75,747 | 2,515 | 33203 | 11 | containing the Jardin Exotique de Monaco |
| 09 | Moneghetti/ Bd de Belgique (Bd Rainier III-Bd de Belgique) | 107,056 | 3,003 | 28051 | 18 | |
| New land reclaimed from the sea | ||||||
| 06 | Fontvieille | 324,157 | 3,292 | 10156 | 9 | started 1971 |
| 11 | Le Portier | 275,000(1) | – | - | - | plans put on hold by Prince Albert II in 2009 |
| Monaco | 1,974,444 | 32,020 | 16217 | 173 | ||
| (1) Area not included in total, as it is only proposed | ||||||
Note: for statistical purposes, the wards of Monaco are further subdivided into 173 city blocks (îlots), which are comparable to the census blocks in the United States.
[edit] History

Monaco's name comes from the 6th century BC nearby Phocaean Greek colony. Referred to the Ligurians as Monoikos, from the Greek "μόνοικος", "single house", from "μόνος" (monos) "alone, single"[8] + "οἶκος" (oikos) "house",[9] which bears the sense of a people either settled in a "single habitation" or of "living apart" from others. According to an ancient myth, Hercules passed through the Monaco area and turned away the previous gods. As a result, a temple was constructed there, the temple of Hercules Monoikos. Because the only temple of this area was the "House" of Hercules, the city was called Monoikos.[10][11]
Following a land grant from Emperor Henry VI in 1191, Monaco was re-founded in 1215 as a colony of Genoa. Monaco has been ruled by the House of Grimaldi since 1297, when Francesco Grimaldi ("Il Malizia", translated from Italian either as "The Malicious One" or "The Cunning One") and his men captured the fortress protecting the Rock of Monaco while he was dressed as a Franciscan monk – a Monaco in Italian, although this is a coincidence as the area was already known by this name.
In 1793, French Revolutionary forces captured Monaco, and it remained under French control until 1814. The principality was re-established that year, only to be designated a protectorate of the Kingdom of Sardinia by the Congress of Vienna in 1815. Monaco remained in this position until 1860, when by the Treaty of Turin, Sardinia ceded to France the surrounding county of Nice (as well as Savoy). During this time there was unrest in the towns of Menton and Roquebrune, which declared independence, hoping for annexation by Sardinia. The unrest continued until the ruling prince gave up his claim to the two towns (some 95% of the country), and they were ceded to France in return for four million francs. This transfer and Monaco's sovereignty was recognised by the Franco-Monegasque Treaty of 1861.
[edit] 20th century
Until the Monegasque Revolution of 1910 forced the adoption of the 1911 constitution, the princes of Monaco were absolute rulers. In July 1918, a treaty was signed providing for limited French protection over Monaco. The treaty, part of the Treaty of Versailles, established that Monegasque international policy would be aligned with French political, military, and economic interests.
In 1943, the Italian army invaded and occupied Monaco, setting up a Fascist administration. Shortly thereafter, following Mussolini's collapse in Italy, the Nazi German Wehrmacht occupied Monaco and began the deportation of the Jewish population. The prominent French Jew René Blum (Paris, 13 March 1878 – Auschwitz, 30 April 1943), who founded the Ballet de l'Opera in Monte Carlo, was arrested in his Paris home and held in the Drancy deportation camp outside Paris, France whence he was then shipped to the Auschwitz concentration camp, where he was killed.

Rainier III, who ruled until 2005, acceded to the throne following the death of his grandfather, Prince Louis II, in 1949. On 19 April 1956, Prince Rainier married the American actress Grace Kelly; the event was widely televised and covered in the popular press, focusing the world's attention on the tiny Principality.
A new constitution in 1962 abolished capital punishment, provided for women's suffrage, and established a Supreme Court of Monaco to guarantee fundamental liberties. In 1993, the Principality of Monaco became a member of the UN, with full voting rights. In 2002, a new treaty between France and Monaco specified that, should there be no heirs to carry on the Grimaldi dynasty, the principality would still remain an independent nation rather than revert to France. Monaco's military defence, however, is still the responsibility of France.
On 31 March 2005, Prince Rainier III, too ill to exercise his duties, relinquished them to his only son and heir, Prince Albert Alexandre Louis. Prince Rainier died on 6 April 2005, after a reign of 56 years, and his son, by Princess Grace, succeeded him as Albert II, Sovereign Prince of Monaco.
Following a period of official mourning, Prince Albert II formally assumed the princely crown on 12 July 2005, in a celebration that began with a solemn Mass at Saint Nicholas Cathedral, where his father had been buried three months earlier. His accession to the Monegasque throne was a two-step event, with a further ceremony, drawing heads of state for an elaborate levée, held on 19 November 2005 at the historic Prince's Palace in Monaco-Ville.
[edit] Law and government
Monaco has been governed under a constitutional monarchy since 1911, with the Sovereign Prince of Monaco as head of state. The executive branch consists of a Minister of State (the head of government), who presides over a five-member Council of Government. Until 2002, the Minister of State was a French citizen appointed by the prince from among candidates proposed by the French government; since a constitutional amendment in 2002, the Minister of State can be French or Monegasque. However, Prince Albert II appointed, on 3 March 2010, the Frenchman Michel Roger as Minister of State.
Under the 1962 constitution, the prince shares his power with the unicameral National Council (parliament). The twenty-four members of this legislative body are elected from lists by universal suffrage for five-year terms. The principality's local affairs are directed by the Communal Council, which consists of fifteen elected members and is presided over by the mayor.
[edit] Economy

One of Monaco's main sources of income is tourism; each year many are attracted to its casino and pleasant climate. Monaco's own citizens are not allowed to gamble in the casino.[12] In 2001, a major new construction project extended the pier used by cruise ships in the main harbour. The principality has successfully sought to diversify into services and small, high-value-added, non-polluting industries, such as cosmetics and biothermics.
The state retains monopolies in numerous sectors, including tobacco and the postal service. The telephone network (Monaco Telecom) used to be fully owned by the state; it now owns only 45%, while the remaining 55% is owned by both Cable & Wireless (49%) and Compagnie Monégasque de Banque (6%). It is still, however, a monopoly. Living standards are high, roughly comparable to those in prosperous French metropolitan areas.[citation needed]
Monaco is not a member of the European Union. However, it is very closely linked via a customs union with France, and as such, its currency is the same as that of France, the euro. Before 2002, Monaco minted its own coins, the Monegasque franc. Monaco has acquired the right to mint euro coins with Monegasque designs on its national side.
[edit] Gambling Industry
Casino gambling was initially legalized during the reign of Florestan I in 1846. At the time, the monarch hoped the newly legal industry would help alleviate the crushing debt the royal family had incurred due in part to economic interference from Sardinia--which had received Monaco as a protectorate under the Treaty of Vienna (1815) and was attempting to destabilize the principality in order to annex it. Monaco's first casino would not receive a royal concession to operate, however, until after Charles III assumed the throne in 1856.[12]
The grantee of this first royal concession was unable to attract enough business to sustain the operation and, after relocating the casino several times, sold the royal concession to French casino magnates François and Louis Blanc for 1.7 million francs. The Blancs had already set up a highly successful casino in Homborg and quickly petitioned Charles III to rename a depressed seaside area known as "Les Spelegures," or "Den of Thieves," "Monte Carlo," or "Mount Charles." They then constructed their casino in the newly dubbed "Monte Carlo" and cleared out the area's less-than-savory elements to make the neighborhood surrounding the establishment more conducive to tourism.
The Blancs opened Le Grand Casino de Monte Carlo in 1858, and the casino benefited from the tourist traffic the newly built French railway system created. Due to the combination of the casino and the railroads, Monaco finally recovered from the previous half century of economic slump, and the principality's success attracted other businesses. In the years following the casino's opening Monaco founded its Oceanographic Museum and the Monte Carlo Opera House, 46 hotels sprang up and the number of jewellers operating in Monaco increased by nearly 500 percent.
Today, Le Grand Casino still operates in the original building the Blancs constructed and has been joined by several other casinos, including Le Casino Café de Paris, the Monte Carlo Bay Casino, the Monte Carlo Sporting Club & Casino (Summer Casino) and the Sun Casino. The most recent addition to the list—the first casino to open in Monte Carlo in 75 years—is the Monte Carlo Bay Casino, which sits on 4 hectares of the Mediterranean Garden and, among other things, offers 145 slot machines, all equipped with "Ticket in/ Ticket out" (TITO); it is the first Mediterranean casino to utilize this technology.[13]
[edit] Tax haven
Monaco levies no income tax on individuals. The absence of a personal income tax in the principality has attracted to it a considerable number of wealthy "tax refugee" residents from European countries who derive the majority of their income from activity outside Monaco; celebrities such as Formula One drivers attract most of the attention, but the vast majority of them are less well-known business people.[citation needed]. This applies to all residents of Monaco of any nationality except French citizens whose residency started after 1957. These French citizens still must pay French income tax.
In 1998, the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) issued a first report on the consequences of the tax havens' financial systems. Monaco did not appear in the list of these territories until 2004, when OECD became indignant regarding the Monegasque situation and denounced it in its last report, as well as Andorra, Liechtenstein, Liberia and the Marshall Islands, underlining its lack of co-operation as regards financial information disclosure and availability.[14][15]
In 2000, a report by the French parliamentarians, Arnaud Montebourg and Vincent Peillon, alleged that Monaco had lax policies with respect to money laundering, including within its famed casino, and that the government of Monaco had been placing political pressure on the judiciary, so that alleged crimes were not being properly investigated.[16]
In 2000, the Financial Action Task Force on Money Laundering (FATF) stated: "The anti-money laundering system in Monaco is comprehensive. However, difficulties have been encountered with Monaco by countries in international investigations on serious crimes that appear to be linked also with tax matters. In addition, the FIU of Monaco (SICCFIN) suffers a great lack of adequate resources. The authorities of Monaco have stated that they will provide additional resources to SICCFIN."[17] The Principality is no longer blamed in the 2005 FATF report, as well as all other territories.[18][19] However, since 2003, the International Monetary Fund (IMF) has identified Monaco, along with 36 other territories, as a tax haven.[20]
The Council of Europe also decided to issue reports naming tax havens. Twenty-two territories, including Monaco, were thus evaluated between 1998 and 2000 on a first round. Monaco is the only territory that refuses to perform the second round, initially forecast between 2001 and 2003, whereas the 21 other territories are implementing the third and last round, planned between 2005 and 2007.[21]
However, Monaco has high social insurance taxes payable by both employer and employee. The employer's contribution is between 28%–40% (averaging 35%) of gross salary including benefits and the employee pays a further 10%–14% (averaging 13%).[22] Social insurance contributions, amounting to nearly 50% of salary, are a major disincentive to the hiring of staff and in many ways detract substantially from the advantageous income tax regime which exists in Monaco[citation needed].
[edit] Numismatics
In Monaco, the euro was introduced in 2002. In preparation for this date, the minting of the new euro coins started as early as 2001. This is why the first euro coins from Monaco have the year 2001 on them, instead of 2002, like other countries of the Eurozone. Three different designs were selected for the Monegasque coins. In 2006, the design was changed after the death of ruling Prince Rainier to have the effigy of Prince Albert.
Monaco also has a rich and valuable collection of collectors' coins, with face value ranging from €5 to €100. These coins are a legacy of an old national practice of minting silver and gold commemorative coins. Unlike normal issues, these coins are not legal tender in all the Eurozone. For instance, a Monegasque commemorative coin cannot be used in any other country. The same practice concerning commemorative coins is exercised with all eurozone countries. Commemorative coins are legal tender only in their country of issue, unlike normal circulation coins, which are accepted in all euro-zone countries.
[edit] Geography
With a total area of 2.02 square kilometres (0.78 sq mi), a land border of 5.469 kilometres (3.4 mi) and a coast measuring 3.829 kilometres (2.4 mi)[3] the Principality of Monaco is the second-smallest independent state in the world, after the Vatican City. It lies on the coast of the Mediterranean Sea, 18 kilometres (11 mi) east of Nice, France, and is surrounded on three sides by France and on the fourth by the sea into which its maritime claims extend to 22.2 kilometres (13.8 mi). Its highest point is 163 metres (535 ft) above sea level, on the southern slopes of Mont Agel whose 1,109 m (3,638 ft) peak is in France. The country has no natural resources.
[edit] Climate
Monaco has a warm-summer Mediterranean climate (Köppen climate classification: Csa), which is influenced by the oceanic climate and the humid subtropical climate.
As a result, it has warm, dry summers and mild, rainy winters. Cool and rainy interludes can interrupt the dry summer season, the average length of which is also shorter. Summer afternoons are infrequently hot (indeed, temperatures > 30 °C /86 °F are rare) as the atmosphere is temperate by constant sea breezes. On the other hand, the nights are very mild, this being due to the fairly high temperature of the sea in summer. Generally, temperatures do not drop below 20 °C in this season. In winter, frosts and snowfalls are extremely rare, generally occurring once or twice every ten years.
| [hide]Climate data for Monaco | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Average high °C (°F) | 12.3 (54.1) | 12.5 (54.5) | 14.0 (57.2) | 16.1 (61) | 19.4 (66.9) | 23.0 (73.4) | 25.8 (78.4) | 25.9 (78.6) | 23.8 (74.8) | 19.9 (67.8) | 16.1 (61) | 13.4 (56.1) | 18.5 (65.3) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 10.2 (50.4) | 10.4 (50.7) | 11.8 (53.2) | 13.9 (57) | 17.1 (62.8) | 20.8 (69.4) | 23.5 (74.3) | 23.7 (74.7) | 21.6 (70.9) | 17.8 (64) | 14.0 (57.2) | 11.4 (52.5) | 16.4 (61.5) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 8.1 (46.6) | 8.2 (46.8) | 9.6 (49.3) | 11.6 (52.9) | 14.8 (58.6) | 18.5 (65.3) | 21.2 (70.2) | 21.5 (70.7) | 19.3 (66.7) | 15.6 (60.1) | 11.9 (53.4) | 9.3 (48.7) | 14.1 (57.4) |
| Precipitation mm (inches) | 82.7 (3.256) | 76.4 (3.008) | 70.5 (2.776) | 62.2 (2.449) | 48.6 (1.913) | 36.9 (1.453) | 15.6 (0.614) | 31.3 (1.232) | 54.4 (2.142) | 108.2 (4.26) | 104.2 (4.102) | 77.5 (3.051) | 768.5 (30.256) |
| Avg. precipitation days | 6.8 | 6.4 | 6.1 | 6.3 | 5.2 | 4.1 | 1.9 | 3.1 | 4.0 | 5.8 | 7.0 | 6.0 | 62.7 |
| Sunshine hours | 148.8 | 152.6 | 201.5 | 228.0 | 269.7 | 297.0 | 341.0 | 306.9 | 240.0 | 204.6 | 156.0 | 142.6 | 2,668.7 |
| Source: Monaco website[23] | |||||||||||||
[edit] Sport and entertainment
[edit] Formula One

Since 1929, the Monaco Grand Prix has been held annually in the streets of Monaco. It is considered to be the second-most prestigious automobile race in the world behind only the Indianapolis 500[citation needed]. The erection of the Circuit de Monaco takes six weeks to complete, and the removal after the race another three weeks. The circuit has many elevation changes and tight corners, along with a tunnel. This together with being incredibly narrow and tight makes it perhaps the most demanding Formula One track. Only two drivers have ever crashed into the harbour, the most famous being Alberto Ascari in the 1955 Monaco Grand Prix, just four days before losing his life at Monza. The other was Paul Hawkins, during the 1965 Monaco Grand Prix.
[edit] Monte Carlo Rally
The Monte Carlo Rally has been held since 1911, having originally been held at the behest of Prince Albert I and is, like the principality's Grand Prix, organised by the Automobile Club de Monaco. It has long been considered to be one of the toughest and most prestigious events in rallying and from 1973 to 2008 was the opening round of the World Rally Championship. Since 2009, the rally has served as the opening round of the Intercontinental Rally Challenge, having most recently been run on the 19th-22 January 2011 in celebration of the event's centenary.
[edit] Football (Soccer)
Monaco hosts two major football teams in the principality; men's football club AS Monaco FC and women's football club OS Monaco. AS Monaco plays at the Stade Louis II and competes in the Ligue 1, the top division of French football. The club is historically one of the most successful clubs in France. Because of the popular appeal of living in Monaco and the lack of income tax, many international stars have played for the club, such as Marcelo Gallardo, Jürgen Klinsmann, Oliver Bierhoff, George Weah, John Collins, Fernando Morientes, Thierry Henry, Fabien Barthez, Rafael Márquez, Javier Saviola, David Trezeguet, John Arne Riise, Patrice Evra, Shabani Nonda, Emmanuel Adebayor, Eiður Smári Guðjohnsen, Jan Koller, Victor Ikpeba, Park Chu-Young and Mahamadou Diarra.
The club reached the 2004 UEFA Champions League Final, led by the likes of Dado Pršo, Fernando Morientes, Akis Zikos, and Ludovic Giuly, losing 3–0 to Portuguese team F.C. Porto. The Stade Louis II also plays host to the annual UEFA Super Cup, which is played between the winners of the UEFA Champions League and the UEFA Europa League. The women's team, OS Monaco, competes in the women's French football league system. The club currently plays in the local regional league deep down in the league system, however once played in the Division 1 Féminine in the 1994–95 season, but were quickly relegated. Current French women's international goalkeeper Sarah Bouhaddi had a short stint at the club before going to the Clairefontaine academy.
[edit] Rugby
Monaco's national rugby team, as of March 2010, is 91st in the International Rugby Board rankings.
[edit] Other sports


The Monte Carlo Masters is currently held annually in neighbouring Roquebrune-Cap-Martin, France, as a professional tournament for men as part of tennis' ATP Masters Series. The tournament has been held since 1897. Golf's Monte Carlo Open was also held at the Monte Carlo Golf Club at Mont Agel in France between 1984 and 1992. Monaco has also competed in the Olympic Games, although, as of 2008, no athlete from Monaco has ever won an Olympic medal.
In 2009, the Tour de France, the world's premier bicycle race, started from Monaco with a 15 km closed-circuit individual time trial starting and finishing there on the first day (4 July) and the 182 km second leg starting there on the following day and ending in Brignoles, France.
Monaco also stage part of the Global Champions Tour (International Show-jumping). Acknowledged as the most glamorous of the series, Monaco will be hosting the world's most celebrated riders, including Monaco's own Charlotte Casiraghi, in a setting facing out over the world's most beautiful yachts, and framed by the Port Hercule and Prince's palace. In 2009, the Monaco stage of the Global Champions tour took place between 25 June – 27 June.
The Monaco Marathon is the only marathon in the world to pass through three separate countries, those of Monaco, France and Italy. The 2010 event took place on 21 March. Runners complete the race by returning to the Stade Louis II.Grand Prix is an annual international sports car race through Monte Carlo's elegant streets.
The Monaco Ironman 70.3 triathlon race is an annual event with over 1000 athletes competing and attracts top professional athletes from around the world. The race includes a 1.9 km swim, 90 km bike ride and 21.1 km run.
[edit] Education
[edit] Primary and secondary schools
Monaco has ten state-operated schools, including: seven nursery and primary schools; one secondary school, Collège Charles III;[24] one lycée that provides general and technological training, Lycée Albert 1er;[25] and one lycée that provides vocational and hotel training, Lycée technique et hôtelier de Monte-Carlo.[26] There are also two grant-aided denominational private schools, including Institution François d'Assise Nicolas Barré and Ecole des Sœurs Dominicaines, and one international school, the International School of Monaco.
[edit] Colleges and universities
There is one university located in Monaco:
[edit] Demographics

Monaco's population is unusual in that the native Monegasques are a minority in their own country. The largest proportion of residents are French nationals (28%), followed by Monegasque (21.6%), Italians (19%), Anglos (7.5% UK & 1% USA), and Germans, Swiss, and Belgians (2.5% to 3% each); another 15% is labeled as "other" populations.[27] A Monacoian is the term used to describe a person living in Monaco who is not a citizen of Monaco.[citation needed]
[edit] Religion
[edit] Christian
[edit] Roman Catholic
The official religion is Roman Catholicism, with freedom of other religions guaranteed by the constitution. There are five Roman Catholic parish churches in Monaco and one cathedral, which is the seat of the archbishop of Monaco. The diocese, which has existed since the mid-nineteenth century, was raised to an archbishopric in 1981 as the Archdiocese of Monaco.
[edit] Anglican
There is one Anglican church (St. Paul's Church), located in the Avenue de Grande Bretagne in Monte Carlo. In 2007 this had a formal membership of 135 Anglicans resident in the principality, but was also serving a considerably larger number of Anglicans temporarily in the country, mostly as tourists. The church site also accommodates an English-language library of over 3,000 books.[28] The church is part of the Anglican Diocese of Gibraltar in Europe.
[edit] Jewish
The Association Culturelle Israélite de Monaco (founded 1948) is a converted house containing a synagogue, a community Hebrew school, and a kosher food shop, located in Monte Carlo. The community (approximately 1,500) mainly consists of retired Jews from Britain (40%) and North Africa. One third of the Jewish population there is Ashkenazi, while the other two thirds are Sephardic.[29]
[edit] Security
The wider defence of the nation is provided by France. Monaco has no navy or air force, but on both a per-capita and per-area basis, Monaco has the largest police force (515 police officers for 35,000 people) and police presence in the world. Its police includes a specialist unit which operates patrol and surveillance boats. There is also a small military consisting of a bodyguard unit for the Prince and his palace called the Compagnie des Carabiniers du Prince which numbers 113 officers and men and is equipped with modern weapons such as M16 rifles and 9 mm pistols, and a militarized (and armed) fire and civil defence Corps.
The Compagnie des Carabiniers du Prince (Prince's Company of Carabiniers) is a military unit of the military force of Monaco. It was created by Prince Honoré IV in 1817 for the protection of the Principality and the Princely family. The company numbers exactly 113 officers and men; while the NCOs and soldiers are local, the officers have generally served in the French Army. Together with the local fire service (Sapeurs-Pompiers), the Carabiniers form Monaco's total public forces. In addition to their guard duties, the company patrols the Principality's beaches and coastal waters, as well as duties around the Palace in Monaco-Ville.
[edit] Flag
The flag of Monaco is one of the world's oldest national flag designs. The flag of Monaco is identical to flag of Indonesia, except for the ratio of height to width.[30]
| This section requires expansion. |
[edit] Transport
Monaco is served by several train systems and the Monte Carlo International Heliport. The closest airport is Côte d'Azur Airport in Nice, France. Some airlines marketed Monaco via Nice Airport.[31]
| This section requires expansion. |


![Location of Monaco (green)on the European continent (dark grey) — [Legend]](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/f/f5/Location_Monaco_Europe.png/250px-Location_Monaco_Europe.png)










No comments:
Post a Comment