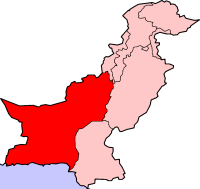
-Flag Of Baluchistan-
Balochistan (Balochi, Urdu: بلوچستان, Brahui: Balocistán) is the largest province (by area) of Pakistan, constituting approximately 44% of the total land mass of Pakistan. According to the 1998 census, Balochistan had a population of roughly 6.6 million.[2]
Its neighbouring regions are Iran to the west; Afghanistan and Khyber Pakhtunkhwa to the north; and Punjab and Sindh to the east. To the south lies the Arabian Sea. The main languages in the province are Balochi, Brahui, Pashto, Sindhi and Urdu.[3] The provincial capital is Quetta and Gwadar is the developing port city .[3] Balochistan is rich in mineral resources; it is the second major supplier of natural gas in Pakistan.
[edit] Geography and climate
Balochistan is located at the south-eastern edge of the Iranian plateau. It strategically bridges the Middle East and Southwest Asia to Central Asia and South Asia, and forms the closest oceanic frontage for the land-locked countries of Central Asia.
In terms of geographical size, Balochistan is the largest of the five provinces of Pakistan at 347,190 km² (134,051 mi²), which composes approximately 44% of the total land area of Pakistan. The population density is very low due to the mountainous terrain and scarcity of water. The southern region is known as Makran. The central region is known as Kalat.
The Sulaiman Mountains dominate the northeast corner and the Bolan Pass is a natural route into Afghanistan towards Kandahar, used as a passageway during the British campaigns to Afghanistan.[4] Much of the province south of the Quetta region is sparse desert terrain with pockets of towns mostly near rivers and streams.
The capital, Quetta, is located in the most densely populated district in the northeast of the province. It is situated in a river valley near the border with Afghanistan, with a road to Kandahar in the northwest.
Very cold winters and hot summers characterise the climate of the upper highlands. Winters of the lower highlands vary from extremely cold in Ziarat, Quetta, Kalat, Muslim Baagh and Khanozai the northern districts to mild conditions closer to the Makran coast. Summers are hot and dry, especially the arid zones of Chaghai and Kharan districts. The plain areas are also very hot in summer with temperatures rising as high as 50 °C (122 °F).The highest record breaking temperature of 53 °C (127 °F) has been recorded in Sibi on 26 May 2010.[5] Previously 52 °C (126 °F) has been recorded in sibi. Other hot areas includes, Turbat, and Dalbandin. Winters are mild on the plains with the temperature never falling below the freezing point. The desert climate is characterised by hot and very arid conditions. Occasionally strong windstorms make these areas very inhospitable.
[edit] Demographics
Main article:
Baloch peopleAs of the 1998 census, Balochistan had a population of 6.6 million inhabitants, representing approximately 5% of the Pakistani population.[2] Official estimates of Balochistan's population grew from approximately 7.45 million in 2003[3] to 7.8 million in 2005.[1] According to the 2008 Pakistan Statistical Year Book, households whose primary language is Balochi represent 40% of Balochistan's population while 20% of households speak Brahvi,and up to 25% speaks Pashtu making Balochi,Brauhi and Pashtu the three dominant languages in the region. Other languages include, Sindhi, Punjabi, and Saraiki.[6] Balochi-speaking people are concentrated in the sparsely populated west, east, south and southeast; Brahui speakers dominate in the center of the province, while the Pashtuns are the majority in the north. The Kalat and Mastung areas speak Brahui. Quetta, the capital of the province, is largely populated with pashtoons people, with a significant pashtoon presence. In the Lasbela District, the majority of the population speaks Sindhi, Balochi, or Lasi. Sindhi is also widely spoken in the Nasirabad District and the cities of Sibi and Dera Murad Jamali.[citation needed] A large number of Afghan refugees moved to Quetta after the Soviet invasion of Afghanistan in 1979. Near the Kalat region and other parts of the province there are significant numbers of Baloch Brahui speakers. Along the coast various Makrani Balochi speakers predominate. A large number of Afghan refugees can also be found in the province, including Pashtuns, Hazaras and Tajiks. Many Sindhi farmers have moved to the more arable lands in the east.[citation needed]
| Historical populations |
| Census | Population | Urban |
|
| 1951 | 1,167,167 | 12.38% |
| 1961 | 1,353,484 | 16.87% |
| 1972 | 2,428,678 | 16.45% |
| 1981 | 4,332,376 | 15.62% |
| 1998 | 6,565,885 | 23.89% |
[edit] Society and culture
Balochistani culture is primarily tribal, deeply patriarchal and conservative. Baloch society is dominated by tribal chieftains called Mirs, Sardars and Nawabs, who are the ruling elite of Balochistan and have been criticized for blocking the educational development and empowerment of the Baloch people[citation needed][weasel words] lest the status quo be challenged.
Honor killings are commonplace[7] but still discouraged by the majority of the population[citation needed]. In one recent incident in August 2008, the Asian Human Rights Commission reported that five women (including three teenagers) in a remote village had been beaten, shot and buried alive in a ditch for the crime of seeking to choose their own husbands. One of the tribesmen involved was the younger brother of a provincial minister from the ruling Pakistan People's Party, and local police therefore refused to take any action.[8]
After human rights activists brought the case to national and international attention, Israr Ullah Zehri of the Balochistan National Party, who represents Balochistan in the Pakistani Parliament, defended the killings and asked his fellow legislators not to make a fuss about the incident. He told Parliament, "These are centuries-old traditions, and I will continue to defend them. Only those who indulge in immoral acts should be afraid." But many Baloch literate oppose these practices. According to majority of Baloch, the person or tribe head should be brought to the court and must be punished. Many Baloch or Balochis have denied the fact that Karo Kari is part of Balochi culture. They claim it was a nomadic cultural practice which was stopped many years ago, but because of poor administration by the Pakistani government and to demilitarize the Baloch, such acts are now taking place.[9]
[edit] History
Balochistan was the site of the earliest known farming settlements in the Indus Valley Civilization, the earliest of which was Mehrgarh dated at 6500 BCE. Balochistan in Pashto is known as 'Godar which was hellenized to Gedrosia due to the fact that the Greeks derived the names of these Iranian lands from the Bactrian language. The Balochi people referred to their own land as Moka or Maka, a word which later became Makran. The word Balochistan is derived from the Persian language and was originally termed to mean "ignorant". However, with the spread of the Persian language, the name Balochistan seems to have stuck. Balochistan was seemingly always sparsely populated by various tribes of Iranic origin for centuries following the decline of the nearby Harappa-Mohenjo-daro civilization to the east. The spread of the Balochi language led to the eventual decline in the numbers of Brahui the original Arachosian tribes of the region.
The Baloch began to arrive from their original homeland in the northwest Zagros Mountains, in Syria, Anatolia and Iran, claiming to be an offshoot of the Medes and the Kurds who would mainly populate the western end of the Iranian plateau. Under influence of Islam, many Baloch—like their neighbors the Pashtuns—believed that their origins were Semitic and not Indo-European Iranic. This stands contrary to linguistic and historical evidence. The Baloch claim that they left their original homeland in far northwestern Zagros Mountains around Aleppo, Syria at some point in the 1st millennium CE and moved to Balochistan.[10] They are considered to be an Iranic group that has absorbed some Semitic genes and cultural traits. The great Persian epic of Shahnama does record the Baloch in the Qazvin-Zanjan region of Persia in the 6th century AD, when they were engaged in battle by the Persian king Chosroes I Anoshervan, apparently at the exact time when the Baloch were making their long distance trek from their old homeland in northwestern Iranian Plateau to the current one, in southeastern parts of the region known today as Balochistan. The immigrating Baloch tribes eventually absorbed all the local people in Makran, southern Sistan and the Barahui country, becaming a sizeable group to rival in size the other Iranic group in the region, the Pashtuns.
The large district and tribe of Belijan/Beluchan still exist in northwest Zagros, stetching from just east of Sivas, south toward Aleppo. The current inhabitants and the tribe identify themselves as Kurds—the cultural and linguistic cousins of the modern Baloch.
In the 7th century, the region was divided into two parts: the south was made part of the Kermān Province of the Persian Empire and the north became part of the Persian province Sistan. In early 644, the Islamic Caliph, Umar, sent Suhail ibn Adi from Busra to conquer the Kerman region of Iran. He was then made governor of that region. From Kerman, he conquered the western Balochistan region, near the Persian frontiers.[11] South-western Balochistan was conquered during the campaign in Sistan the same year.
During the reign of Caliph Uthman in 652, Balochistan was reconquered during the counter-revolt in Kerman, under the command of Majasha Ibn Masood. This was first time western Balochistan became directly controlled by the Caliphate and paid taxes on agriculture.[12] In those days western Balochistan was included in the dominion of Kerman. In 654, Abdulrehman ibn Samrah, governor of Sistan, sent an Islamic army to crush a revolt in Zaranj, which is now in southern Afghanistan. After conquering Zaranj, a column of the army pushed north, conquering Kabul and Ghazni, in the Hindu Kush mountain range, while another column moved through North-western Balochistan and conquered the area up to the ancient city of Dawar and Qandabil (Bolan).[13] By 654, the whole of what is now the Balochistan province of Pakistan was controlled by the Rashidun Caliphate, except for the well-defended mountain town of QaiQan which is now Kalat. However, this town was later conquered during the reign of Caliph Ali.[14] Abdulrehman ibn Samrah made Zaranj his provincial capital and remained governor of these conquered areas from 654 to 656, until Uthman was murdered.
During the Caliphate of Ali, a region of Balochistan, Makran, again revolted. Due to civil war in the Islamic empire, Ali was unable to deal with these areas until 660, when he sent a large force, under the command of Haris ibn Marah Abdi, towards Makran and Sind. Haris ibn Marah Abdi arrived in Makran and conquered it by force, and then moved northward to north-eastern Balochistan and reconquered Qandabil (Bolan). Finally, he moved south and conquered Kalat after a fierce battle.[15] In 663, during the reign of Umayyad Caliph Muawiyah I, Muslims lost control of North-eastern Balochistan and Kalat when Haris ibn Marah and large part of his army died in battle against a revolt in Kalat.[16] Muslim forces later regained control of the area during Umayyad reign. It also remained a part of the Abbasid Caliphate.
In the 15th century, Mir Chakar Khan Rind became the first king of Balochistan. Subsequently, Balochistan was dominated by the Timurids, who controlled all of Persia and Afghanistan. The Mughal Empire also controlled some parts of the area. When Nadir Shah won the allegiance of the rulers of Balochistan, he ceded Kalhora, one of the Sindh territories of Sibi-Kachi to the Khan of Kalat.[17][18][19] The successor of Nadir Shah and founder of the Afghan Empire, Ahmad Shah Durrani, also won the allegiance of that area's rulers. Most of the area would eventually revert to local Baloch control, however, parts of the northern regions would continue to be dominated by Pashtun tribes.
During the period of the British Raj, there were four Princely States in Balochistan: Makran, Kharan, Las Bela and Kalat. In 1876, Sir Robert Sandeman made a treaty with the Khan of Kalat and brought his territories (including Kharan, Makran, and Las Bela) under British suzerainty. After the Second Afghan War was ended by the Treaty of Gandamak in May 1879, the Afghan Emir ceded the districts of Quetta, Pishin, Sibi, Harnai, and Thal Chotiali to the British. In 1883, the British took control of the Bolan Pass, southeast of Quetta, from the Khan of Kalat. In 1887, some of the areas of Balochistan were declared British territory. In 1893, Sir Mortimer Durand negotiated an agreement with the Amir of Afghanistan, Abdur Rahman Khan, to fix the Durand Line running from Chitral to Balochistan as the boundary between the Emirate of Afghanistan and the British.
Two devastating earthquakes occurred in Balochistan during the British colonial rule: The 1935 Balochistan Earthquake, which devastated Quetta, and the 1945 Balochistan Earthquake, which, with its epicentre in the Makran region, was felt in other regions of South Asia.
After independence from the British, Balochistan, like much of Pakistan, has experienced development. However, due to its sparse population, it has developed at a much slower rate than other parts of Pakistan. This has led to the conflict in Balochistan.
[edit] Government
In common with the other provinces of Pakistan, Balochistan has a parliamentary form of government. The ceremonial head of the province is the Governor, who is appointed by the President of Pakistan on the advice of the provincial Chief Minister. The chief executive of the province is the Chief Minister who is normally the leader of the largest party or alliance in the provincial assembly. The unicameral Provincial Assembly of Balochistan comprises 65 seats of which 4% are reserved for non-Muslims and 16% for women only. The judicial branch of government is carried out by the Balochistan High Court, based in Quetta, and headed by a Chief Justice. For administrative purposes, the province is subdivided into 30 districts:[20]
[edit] Economy
Balochistan's share of the national economy has historically ranged between 3.7% to 4.9%.[21] Since 1972, Balochistan's economy has grown in size by 2.7 times.[22] The economy of the province is largely based upon the production of natural gas, coal and minerals. Outside Quetta, the infrastructure of the province is gradually developing but still lags far behind other parts of Pakistan. Tourism remains limited but has increased due to the exotic appeal of the province. Limited farming in the east as well as fishing along the Arabian Sea coastline are other forms of income and sustenance for the local populations. Due to the tribal lifestyle of many Baloch and Brahui, animal husbandry is important, as are trading bazaars found throughout the province.
Though the province remains largely underdeveloped, there are currently several major development projects in progress in Balochistan, including the construction of a new deep sea port at the strategically important town of Gwadar.[23] The port is projected to be the hub of an energy and trade corridor to and from China and the Central Asian republics.
Further west is the Mirani Dam[24] multipurpose project, on the Dasht River, 50 kilometres (31 mi) west of Turbat in the Makran Division. It will provide dependable irrigation supplies for the development of agriculture and add more than 35,000 km² of arable land. There is also Chinese involvement in the nearby Saindak gold and copper mining project.
One of the world's largest copper deposits (and its matrix-associated residual gold) have been found at Reko Diq in the Chagai District of Balochistan. Reko Diq is a giant mining project in Chaghi. The main license (EL5) is held jointly by the Government of Balochistan (25%), Antofagasta Minerals (37.5%) and Barrick Gold (37.5%). The deposits at Reko Diq are hoped to be even bigger than those of Sarcheshmeh in Iran and Escondida in Chile (presently, the second and the third largest proven deposits of copper in the world).[citation needed]
BHP Billiton, the world's largest copper mining company, began the project in cooperation with the Australian firm Tethyan, entering into a joint venture with the Balochistan government. The potential annual copper production has been estimated to be 900,000 to 2.2 million tons.[citation needed] The deposits seem to be largely of porphyry rock nature.[citation needed]
[edit] Education
Balochistan's notable institutions of higher learning include: Balochistan University of Engineering and Technology (Khuzdar), Balochistan University of Information Technology Engineering and Management Sciences (Quetta), Bolan Medical College (Quetta), Iqra University (Quetta), Sardar Bahadur Khan Women University (Quetta), Tameer-e-Nau Public College, Quetta, and University of Balochistan (Quetta).
Balochistan has the lowest Human Development Index of all the provinces of Pakistan at 0.556.[25] Balochistan's rural areas have one of the lowest literacy rates in Pakistan; around 90% of rural females in Balochistan are illiterate. Almost all the districts of Balochistan have a literacy rate below 50% and some are below 35%. The districts with the lowest literacy rate are Musakhel (14%), Nasirabad (15%), Kohlu (17%), Jhal Magsi (17%), Kharan (19%), Awaran (20%), Bolan (21%), Killa Saifullah (24%) and Jafarabad (25%).[26]
However, Balochistan's overall literacy has improved significantly over the past 30 years, as shown in the table below.
| Year | Literacy rate[26][27] |
| 1972 | 10.1% |
| 1981 | 10.3% |
| 1998 | 26.6% |
| 2008 | 48.8% |
| Qualification[28] | Urban | Rural | Total | Enrolment ratio (%) |
| — | 1,568,780 | 4,997,105 | 6,565,885 | — |
| Below Primary | 237,827 | 1,149,334 | 1,387,161 | 10.00 |
| Primary | 361,760 | 1,427,173 | 1,788,933 | 15.87 |
| Middle | 325,051 | 971,437 | 1,296,488 | 17.62 |
| Matriculation | 318,932 | 846,509 | 1,165,441 | 31.88 |
| Intermediate | 132,248 | 232,865 | 365,113 | 14.13 |
| BA, BSc... degrees | 9,726 | 16,490 | 26,216 | 8.57 |
| MA, MSc... degrees | 99,303 | 133,422 | 232,725 | 8.17 |
| Diploma, Certificate... | 56,319 | 61,464 | 117,783 | 4.62 |
| Other qualifications | 27,614 | 158,411 | 186,025 | 2.83 |
[edit] See also-(copy of wikipedia)
![[Flag of the Cordillera People]](http://www.fotw.net/images/p/ph-cpdf.gif)